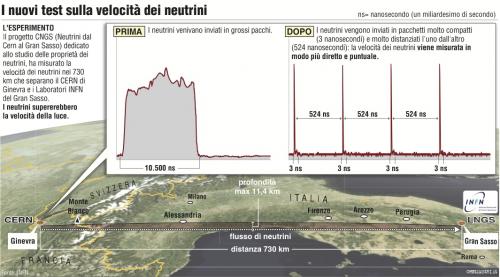
It is not yet a final confirmation, but the hypothesis that neutrinos actually go "faster than light" is gaining strength. Following a new experiment conducted inside OPERA, it is now possible to exclude some potential errors that could have been ascribed to previous measurements. In the new test, the beams of neutrinos sent from CERN were shorter in time and spaced farther apart; they were then analyzed at the Gran Sasso National Laboratories. The new bundles are characterized by "a better definition of the extraction time of protons. That is, the neutrinos packets are only 3 nanoseconds long and spaced from each other by 524 nanoseconds. They are much narrower and more spaced compared to those of the announced result in September: in that case, the beams lasted 10 500 nanoseconds and were separated by 50 million nanoseconds" according to declarations by the National Institute of Nuclear Physics.
"Such a crucial measurement, that has profound implications for physics, requires an exceptional level of detail," said Fernando Ferroni, new president of the National Institute of Nuclear Physics. "The OPERA experiment, thanks to the special adjustment of the neutrino beams provided by CERN, has produced an important test for the consistency of its results. The positive outcome of the tests makes us more confident about the results, but the final say will have to wait until additional similar experiments are conducted in other parts of the world. "
The study, which describes in detail the new measurement, was submitted to JHEP magazine, and is available on the arXiv website as from today (November 18).
Arxiv website

