The effectiveness of the pandemic H1N1 influenza vaccination program, introduced in Scotland in October 2009, has been assessed by a team of researchers from different Scottish and French institutions, coordinated by Dr. Colin Simpson, from the University of Edinburgh. The results of this assessment has been published in the June issue of Lancet.
The vaccination campaign consisted of two phases, the first being aimed at frontline health-care workers, pregnant women and people whose underlying health problems make them more sensitive to influenza-like illness; in the second phase, all children aged between 6 months and 5 years were targeted.
The researchers performed a retrospective study by linking primary care, hospital records and death certification datasets of 247178 persons, representing the 5% of Scottish population. Of them, 38296 (15.5%) were given the vaccination. In this nationally representative cohort there were fewer hospital admissions and deaths from influenza-like illness – influenza, pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and cardiac disorders – in patients who were vaccinated against H1N1 influenza A virus. A representative sub-group of patient was swabbed and tested with RT-PCR, revealing an estimated vaccine effectiveness of 77%. Such a result proved to be higher than recent estimates in case-control studies undertaken in the UK (72%) and Europe (71.9%) but lower than another one performed in Navarre, Spain (89%).
The study thus provided evidence that the Scottish H1N1 vaccination program have been effective, both in terms of protection against the virus and reduction of mortality from influenza-like illness, and is likely to have reduced the burden of pandemic influenza on health-care providers.
Effectiveness in Scotland
Primary tabs
prossimo articolo
Why have neural networks won the Nobel Prizes in Physics and Chemistry?
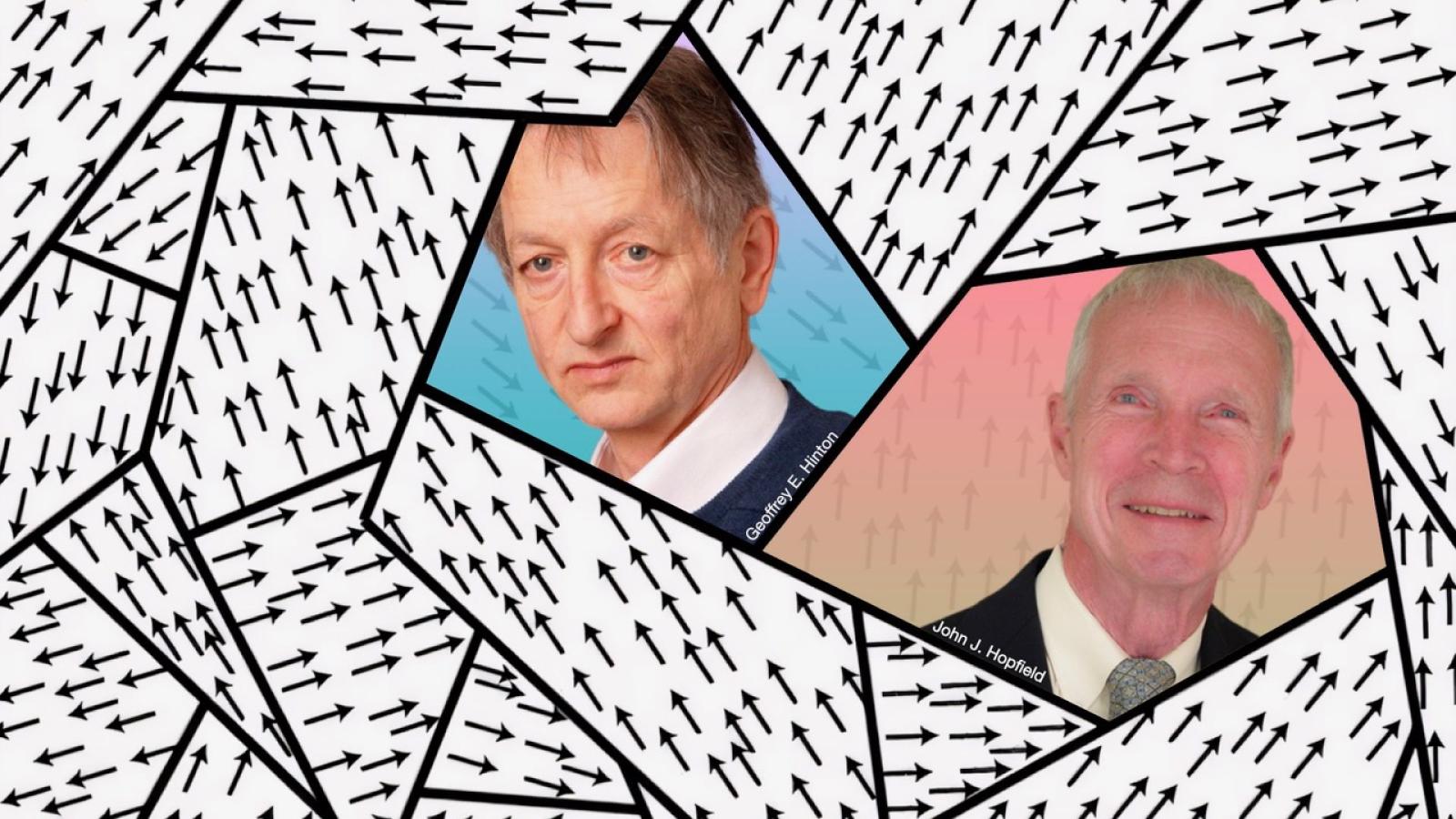
This year, Artificial Intelligence played a leading role in the Nobel Prizes for Physics and Chemistry. More specifically, it would be better to say machine learning and neural networks, thanks to whose development we now have systems ranging from image recognition to generative AI like Chat-GPT. In this article, Chiara Sabelli tells the story of the research that led physicist and biologist John J. Hopfield and computer scientist and neuroscientist Geoffrey Hinton to lay the foundations of current machine learning.
Image modified from the article "Biohybrid and Bioinspired Magnetic Microswimmers" https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1002/smll.201704374
The 2024 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to John J. Hopfield, an American physicist and biologist from Princeton University, and to Geoffrey Hinton, a British computer scientist and neuroscientist from the University of Toronto, for utilizing tools from statistical physics in the development of methods underlying today's powerful machine learning technologies.
